Popular Articles (May 2016)
-
1. A Low-Power Incremental Delta–Sigma ADC for CMOS Image Sensors
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):371 - 375This brief presents a second-order incremental delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for CMOS image sensors (CISs). The ADC that employs a cascade of integrators with a feedforward architecture uses only one operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) by sharing the OTA between the first and second stages of the modulator. Further power and area savings are achieved by using a self-biasin... View full abstract»

-
2. Design Techniques for Linearity in Time-Based
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):433 - 437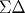
Due to technology scaling, the design of the conventional-type analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which uses an operational amplifier as one of its building blocks, becomes more difficult. In this brief, new techniques to design time-based ADC (TADC), which uses a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), are proposed. The VCO is followed by a time-to-digital converter, implemented in a ΣΔ... View full abstract»

-
3. CMOS Transimpedance Amplifier for Gigabit-per-Second Optical Wireless Communications
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):418 - 422A variable-gain current-amplifier-based feedback transimpedance amplifier (CA-TIA) with a gain-insensitive bandwidth is analyzed and designed for gigabit-per-second optical wireless communications. Implemented in 0.18-μm CMOS, as the transimpedance gain varies from 55.8 to 69.3dBΩ, the 3-dB bandwidth of the CA-TIA remains relatively invariable around 1 GHz. View full abstract»

-
4. An Amplifier-Free Pipeline-SAR ADC Architecture With Enhanced Speed and Energy Efficiency
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):341 - 345A new pipeline-successive approximation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) structure without residue amplifier and timing-interleaving is presented in this brief. Two redistribution digital-to-analog converters (DACs) and comparators are adopted in two stages, with DAC1 for most significant bit (MSB) comparisons and DAC2 for least significant bit (LSB) compariso... View full abstract»

-
5. A 0.5-V 1.3-
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):523 - 527This brief presents a low-power analog acquisition front-end circuit for a Wireless Body Area Network. This front-end system mainly consists of three parts, namely, chopped capacitively coupled instrumentation amplifier (CCIA), switched capacitor filter (SC-filter), and successive-approximation analog-to-digital converter. In order to reduce the power consumption, the supply voltage is scaled to 0... View full abstract»

-
6. A Low-Voltage PLL With a Supply-Noise Compensated Feedforward Ring VCO
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):548 - 552A low-voltage phase-locked-loop (PLL) circuit with a supply-noise-compensated feedforward ring voltage-controlled oscillator (FRVCO) is demonstrated. The oscillation frequency fluctuation due to supply noise is compensated by adjusting the ratio of driving strength in feedforward and direct paths in FRVCO. A prototype 400-MHz PLL circuit operating at 0.65 V is fabricated with 180-nm standard CMOS ... View full abstract»

-
7. A Simplified Model for Passive-Switched-Capacitor Filters With Complex Poles
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):513 - 517This brief demonstrates a method to realize complex conjugate poles using passive-switched-capacitor networks. In addition, a simplified continuous-time model will be introduced so that accurate transfer functions and output noise can be obtained without the need for complicated charge-balance equations and thereby allow a better intuitive understanding of these structures. The developed theory is... View full abstract»

-
8. A 12.5 mW, 11.1
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):443 - 447
A driver amplifier suitable for integration with an 18 bit 500 kS/s successive approximation register analog-todigital converter (ADC) is reported. It accepts single-ended or fully differential inputs. The driver consumes 12.5 mW from a 5 V supply, has a -115 dB (-120 dB) total harmonic distortion for 8 Vppd output at 1 kHz (10 kHz), a 240 ns settling time to 0.01% accuracy for a 2 Vppd output ste... View full abstract»

-
9. A Two-Stage Broadband Fully Integrated CMOS Linear Power Amplifier for LTE Applications
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):533 - 537This brief presents the implementation and measurement results of a CMOS broadband linear power amplifier (PA) for long-term evolution (LTE) applications. Interstage matching considering the main's source and the driver's load impedances is analyzed for broadband linear output power. The proposed PA is fabricated in standard 0.11-μm RF CMOS technology. The PA achieves linear output power of... View full abstract»

-
10. An Accurate Bandgap-Based Power-on-Detector in 14-nm CMOS Technology
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):428 - 432A novel power-on-detector (POD) circuit is reported in 14-nm technology. This POD has a sigma accuracy of 12 mV, including process, voltage, and temperature variations with a power of 496 μW and an area of 0.02 mm2. The POD uses an open-loop offset-cancelled bandgap-based circuit to achieve this high accuracy. It is also capable of detecting two operating voltages simultaneously ... View full abstract»

-
11. A 0.0054-mm2 Frequency-to-Current Conversion-Based Fractional Frequency Synthesizer in 32 nm Utilizing Deep Trench Capacitor
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):413 - 417In this brief, a frequency-to-current conversion-based fractional frequency synthesizer is implemented in 32-nm technology utilizing a high-density deep trench capacitor. The technique proposed here can replace the use of multiple crystal oscillators or a phase-locked loop for medium accuracy clock generation with very low chip area and power consumption. In addition to exploiting the inherently l... View full abstract»

-
12. A Low-Cost Low-Power Ring Oscillator-Based Truly Random Number Generator for Encryption on Smart Cards
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):608 - 612The design of a low-cost low-power ring oscillator-based truly random number generator (TRNG) macrocell, which is suitable to be integrated in smart cards, is presented. The oscillator sampling technique is exploited, and a tetrahedral oscillator with large jitter has been employed to realize the TRNG. Techniques to improve the statistical quality of the ring oscillatorbased TRNGs' bit sequences h... View full abstract»

-
13. Still More on the
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):538 - 542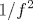
Modeling tank losses in a harmonic oscillator by means of an equivalent parallel resistance may lead to an optimistic estimate of phase noise, as recently experienced in a class-D CMOS oscillator. The discrepancy is significant if two conditions are fulfilled: The single-ended portion of the tank capacitance displays a non-negligible loss, and the loop gain of the oscillator is very large; in the ... View full abstract»

-
14. A Novel Window Function for Memristor Model With Application in Programming Analog Circuits
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):423 - 427A mathematical model for the TiO2 thin-film memristive devices found by Hewlett Packard Labs is proposed in this brief. By taking the current passing through the device into consideration and introducing two adjustable parameters, a novel window function is presented such that the resolution of the boundary lock, full scalability, and nonlinear ionic effects are simultaneously achieved.... View full abstract»

-
15. A Study of Loosely Coupled Coils for Wireless Power Transfer
Publication Year: 2010, Page(s):536 - 540
Cited by: Papers (79)Nonradiative wireless power transfer using magnetically coupled coils is studied in order to transfer a predetermined amount of power at the maximum efficiency. Accordingly, a conceptual wireless power transfer system and a tuning method are presented. Such a study is essential for effectively exploiting the inherent ability of a given pair of coupled coils. With the equations for inductance and r... View full abstract»

-
16. A High Slew-Rate Push–Pull Output Amplifier for Low-Quiescent Current Low-Dropout Regulators With Transient-Response Improvement
Publication Year: 2007, Page(s):755 - 759
Cited by: Papers (58)A high slew-rate amplifier with push-pull output driving capability is proposed to enable an ultra-low quiescent current (Iq ~ 1muA) low-dropout (LDO) regulator with improved transient responses. The proposed amplifier eliminates the tradeoff between small Iq and large slew-rate that is imposed by the tail-current in conventional amplifier design. Push-pull output stage is introduced to enhance th... View full abstract»

-
17. A Self-Calibrated Bang–Bang Phase Detector for Low-Offset Time Signal Processing
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):453 - 457This brief describes a self-calibrated bang-bang phase detector that has been implemented in a delay-locked loop (DLL) stabilized time-to-digital converter for high-energy physics applications. A two-state architecture is proposed, with a dedicated calibration state that measures the internal static phase offset and compensates for this offset in the other measurement state. The calibration is tra... View full abstract»

-
18. A 12.5-ENOB 10-kS/s Redundant SAR ADC in 65-nm CMOS
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):244 - 248This brief describes a 14-b 10-kS/s successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for biomedical applications. In order to achieve enhanced linearity, a uniform-geometry nonbinary-weighted capacitive digital-to-analog converter is implemented. In addition, a secondary-bit approach to dynamically shift decision levels for error correction is employed. To reduce the power consu... View full abstract»

-
19. Wideband TV White Space Transceiver Design and Implementation
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):24 - 28For transceivers operating in television white space (TVWS), frequency agility and strict spectral mask fulfillments are vital. In the U.K., TVWS covers a 320-MHz-wide frequency band in the UHF range, and the aim of this brief is to present a wideband digital up- and downconverter for this scenario. Sampling at radio frequency (RF), a two-stage digital conversion is presented, which consists of a ... View full abstract»

-
20. Metastablility in SAR ADCs
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s): 1The fundamental limitation of Nyquist ADC architectures towards high speed is metastability. It refers to the inability of a latched comparator to produce a valid decision in a certain available time. This issue is usually severe in high-speed Successive-Approximation-Register (SAR) ADCs due to their serial conversion scheme, which includes the regeneration and the reset process of the comparator ... View full abstract»

-
21. Kickback noise reduction techniques for CMOS latched comparators
Publication Year: 2006, Page(s):541 - 545
Cited by: Papers (44) | Patents (1)The latched comparator is a building block of virtually all analog-to-digital converter architectures. It uses a positive feedback mechanism to regenerate the analog input signal into a full-scale digital level. The large voltage variations in the internal nodes are coupled to the input, disturbing the input voltage-this is usually called kickback noise. This brief reviews existing solutions to mi... View full abstract»

-
22. A Sign-Equality-Based Background Timing-Mismatch Calibration Algorithm for Time-Interleaved ADCs
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):518 - 522A background timing-mismatch calibration algorithm is proposed, which detects and corrects the sampling time mismatches in time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter (ADC) channels by analyzing the sign-equality of a reference slope and a timing-mismatch-induced error value. The sign of the ideal derivative along the input is estimated through the adjacent channel outputs, thus not requiring an ... View full abstract»

-
23. A 0.05- to 10-GHz, 19- to 22-GHz, and 38- to 44-GHz Frequency Synthesizer for Software-Defined Radios in 0.13-
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):109 - 113This brief presents a fully integrated frequency synthesizer for software-defined radios covering not only all the existing wireless standards from 47 MHz to 10 GHz [including 14-band multiband orthogonal frequency-division modulation (MB-OFDM) ultrawideband (UWB)] but also the gigabits per second wireless communication around 60 GHz. A dual-band quadrature output voltage-controlled oscillatior re... View full abstract»

-
24. Low-Power ASK Detector for Low Modulation Indexes and Rail-to-Rail Input Range
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):458 - 462A high-performance ultrahigh-frequency amplitude shift keying (ASK) detector for low-power radio-frequency (RF) receivers is proposed. The circuit is based on a high-gain common-source topology with a feedback loop that provides adaptive biasing. Hence, high sensitivity and rail-to-rail input operation are achieved along with low power consumption. The detector was implemented in a standard 130-nm... View full abstract»

-
25. A Wide Input Range Dual-Path CMOS Rectifier for RF Energy Harvesting
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s): 1This paper presents a dual-path CMOS rectifier with adaptive control for ultra-high frequency (UHF) RF energy harvesters. The input power range with high power convention efficiency (high-PCE) of the rectifier is extended by the proposed architecture which includes a low-power path and a high-power path. The dual-path rectifier with an adaptive control circuit is fabricated in a 65 nm CMOS process... View full abstract»

-
26. Phase-domain all-digital phase-locked loop
Publication Year: 2005, Page(s):159 - 163
Cited by: Papers (80) | Patents (11)A fully digital frequency synthesizer for RF wireless applications has recently been proposed. At its foundation lies a digitally controlled oscillator that deliberately avoids any analog tuning controls. When implemented in a digital deep-submicrometer CMOS process, the proposed architecture appears more advantageous over conventional charge-pump-based phase-locked loops (PLLs), since it exploits... View full abstract»

-
27. A Phase-Interpolator based Fractional-Counter for All Digital Fractional-N Phase-Locked Loop
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s): 1A phase-interpolator-based fractional counter (PIFC) is proposed to reduce power consumption by replacing TDC in a ring-oscillator-based digital fractional-N phase-locked-loop. A predicted-phase-interpolation method is used to calculate the integer and fractional parts of the frequency-division-ratio and to find two interpolation clocks; the prediction method gives a significant power reduction in... View full abstract»

-
28. Combined-Step-Size Affine Projection Sign Algorithm for Robust Adaptive Filtering in Impulsive Interference Environments
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):493 - 497This brief proposes a combined-step-size (CSS) affine projection sign algorithm (APSA) to improve the poor tracking capability of the conventional variable-step-size APSA. To achieve a good tracking capability, the variable mixing factor of the proposed CSS-APSA is investigated by using a modified sigmoidal activation function. Meanwhile, the variable mixing factor is indirectly updated by minimiz... View full abstract»

-
29. Direct Mismatch Characterization of Femtofarad Capacitors
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):151 - 155Reducing the capacitance of programmable capacitor arrays (PCAs), commonly used in analog integrated circuits, is necessary for low-energy applications. However, limited mismatch data are available for small capacitors. We report mismatch measurement for a 2-fF poly-insulator-poly (PIP) capacitor, which is the smallest reported PIP capacitor to the best of the authors' knowledge. Instead of using ... View full abstract»

-
30. High Power-Supply-Rejection (PSR) Current-Mode Low-Dropout (LDO) Regulator
Publication Year: 2010, Page(s):868 - 873
Cited by: Papers (19)Modern system-on-a-chip (SoC) solutions suffer from limited on-chip capacitance, which means that the switching events of functionally dense ICs induce considerable noise in the supplies. This ripple worsens the accuracy of sensitive analog electronics, such as ADCs, PLLs, and VCOs, etc. Without dropping a substantial voltage, point-of-load (PoL) low-dropout (LDO) regulators reduce (filter) this n... View full abstract»

-
31. A Memristive Pascaline
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):558 - 562The original Pascaline was a mechanical calculator able to sum and subtract integers. It encodes information in the angles of the mechanical components (such as wheels and cylinders), is aided by gravity, and performs the calculations. Here, we show that such a concept can be realized in electronics using memory elements such as memristive systems. By using memristive emulators, we have demonstrat... View full abstract»

-
32. A 64-Channel 965-
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):528 - 532This brief presents a 64-channel neural recording system-on-chip (SoC) with a 20-Mb/s wireless telemetry. Each channel of the analog front end consists of a low-noise bandpass amplifier, featuring a noise efficiency factor of 3.11 with an input-referred noise of 5.6 μVrms in a 0.001- to 10-kHz band and a 31.25-kSps 6-fJ/conversion-step 10-bit SAR analog-to-digital converter. The ... View full abstract»

-
33. A Fully Integrated Digital LDO With Coarse–Fine-Tuning and Burst-Mode Operation
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):683 - 687The digital low dropout regulator (D-LDO) has drawn significant attention recently for its low-voltage operation and process scalability. However, the tradeoff between current efficiency and transient response speed has limited its applications. In this brief, a coarse–fine-tuning technique with burst-mode operation is proposed to the D-LDO. Once the voltage undershoot/overshoot is detected... View full abstract»

-
34. A 330-
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):448 - 452An energy-efficient 400-MHz binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) transmitter (TX) is proposed for biomedical applications in this brief. The BPSK signal is generated by edge-combining multiple phases from a low-frequency voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), which avoids power-hungry local oscillator generation at RF. Furthermore, the output matching network and edge combiner are merged into a power am... View full abstract»

-
35. A UWB-Based Sensor-to-Time Transmitter for RF-Powered Sensing Applications
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):503 - 507An ultrawideband (UWB)-based sensor-to-time transmitter consisting of a remote control (RC) time-constant interface and an ultralow-power pulse generator is presented. The sensing information is directly extracted and transmitted in the time domain, exploiting UWB pulses with a high timedomain resolution. This approach eliminates the need for an analog-to-digital converter and baseband blocks of s... View full abstract»

-
36. Cooperative Wideband Spectrum Sensing Based on Sub-Nyquist Sparse Fast Fourier Transform
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):39 - 43This brief presents a novel algorithm to perform cooperative wideband spectrum sensing (CWSS) for cognitive radios (CRs). The proposed algorithm is based on a sub-Nyquist version of the sparse fast Fourier transform (sFFT) algorithm, and it is executed cooperatively by using M identical nodes. In this case, we designed a CWSS circuit based on the proposed algorithm that implements the main functio... View full abstract»

-
37. A capacitor cross-coupled common-gate low-noise amplifier
Publication Year: 2005, Page(s):875 - 879
Cited by: Papers (103) | Patents (6)The conventional common-gate low-noise amplifier (CGLNA) exhibits a relatively high noise figure (NF) at low operating frequencies relative to the MOSFET fT, which has limited its adoption notwithstanding its superior linearity, input matching, and stability compared to the inductively degenerated common-source LNA (CSLNA). A capacitor cross-coupled gm-boosting scheme is desc... View full abstract»

-
38. A Metastability Error Detection and Reduction Technique for Partially Active Flash ADCs
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):331 - 335A metastability error detection and reduction technique for partially active analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) is presented. It detects the metastability condition by comparing the coarse ADC output with a predefined voltage level. The metastability of the proposed comparator-based and prior logic gate-based metastability detectors (MDs) is analyzed. The metastable probability of the MD is shown... View full abstract»

-
39. Single-Exposure HDR Technique Based on Tunable Balance Between Local and Global Adaptation
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):488 - 492
Cited by: Papers (1)This brief describes a high-dynamic-range technique that compresses wide ranges of illuminations into the available signal range with a single exposure. An online analysis of the image histogram provides the sensor with the necessary feedback to dynamically accommodate changing illumination conditions. This adaptation is accomplished by properly weighing the influence of local and global illuminat... View full abstract»

-
40. A 14 bit, 30 MS/s, 38 mW SAR ADC Using Noise Filter Gear Shifting
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s): 1We present a SAR ADC that employs a comparator with time varying noise performance, realized by changing the integration time of a Gm-C preamplifier. This approach allows us to relax precision and enhance speed during non-critical decisions, leading to an aggregate speedup of 22% compared to a conventional design. The ADC operates at 30 MS/s, achieves a peak SNDR of 77.2 dB and consumes 38 mW from... View full abstract»

-
41. Charge-Controlled Oscillators and their Application in Frequency Synthesis
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s): 1A tunable oscillator, whose frequency is a function of the total charge in the oscillating nodes, is introduced in this paper. Three variants of charge-controlled oscillators that oscillate around 3.6 GHz are presented. The figure-of-merit(s) of these oscillators, obtained from simulation, are 169 dB, 172 dB and 178 dB. The measured FoM of the third QCO is 179 dB. We also show that the use of a ch... View full abstract»

-
42. An Area-Efficient Current-Mode Bandgap Reference With Intrinsic Robust Start-Up Behavior
Publication Year: 2015, Page(s):937 - 941During mass production, bandgap reference failure can cause chip failure, resulting in yield loss. A bandgap reference with robust start-up behavior is therefore needed. In this brief, the issue of multiple operating points is examined, along with a prior art low-voltage current-mode bandgap reference (CMBGR) structure. A CMBGR structure with only two stable operating points is proposed, which can... View full abstract»

-
43. A Low-Power Two-Tap Voltage-Mode Transmitter With Precisely Matched Output Impedance Using an Embedded Calibration Circuit
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):573 - 577In this brief, a low-power two-tap voltage-mode transmitter (TX) with precisely matched output impedance using an embedded calibration circuit for dc-coupled unidirectional links is proposed. The proposed TX adopts an N-over-N driver with a supply voltage of 0.4 V in order to reduce the power consumption of the output driver. Its output driver is configured as a two-tap Finite Impulse Response (FI... View full abstract»

-
44. DTMOS-Based Pulse Transformer Boost Converter With Complementary Charge Pump for Multisource Energy Harvesting
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):508 - 512An energy-harvesting system that accommodates both discrete-time or continuous-time energy sources simultaneously is presented. The core dc-dc converter is a pulse transformer boost converter using dynamic threshold MOS transistor that self-starts at 36 mV-input voltage and generates bipolar output voltages up to ±2.5 V. Employing the dynamic body bias technique to the boost converter power... View full abstract»

-
45. Low-Complexity Pipelined Architecture for FBMC/OQAM Transmitter
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):19 - 23Filter-bank multi-carrier with offset quadrature amplitude modulation (FBMC/OQAM) is considered by recent research projects as a key enabler for the future 5G air interface. It exhibits better spectrum shape and improves mobility support compared to orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM). Therefore, the availability of efficient hardware implementations becomes of high interest. In this... View full abstract»

-
46. A 55-GHz-Bandwidth Track-and-Hold Amplifier in 28-nm Low-Power CMOS
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):229 - 233This brief presents a 25-GS/s track-and-hold amplifier (THA) implemented in a 28-nm low-power digital CMOS process. Given the intrinsic low-pass behavior of the THA core, a frequency compensation technique is employed to improve the bandwidth by increasing the input amplitude for higher frequencies. This enhances the small-signal bandwidth by almost 30% to 70 GHz. Large-signal measurements show a ... View full abstract»

-
47. A Hybrid-Domain Two-Step Time-to-Digital Converter Using a Switch-Based Time-to-Voltage Converter and SAR ADC
Publication Year: 2015, Page(s):631 - 635In this brief, an energy-efficient time-to-digital converter (TDC) using a hybrid of time- and voltage-domain circuits is presented. The proposed TDC operates in two steps, i.e., first in the time domain by using a delay-line TDC and then in the voltage domain by using a successive-approximation-register analog-to-digital converter. The time residue of the first stage is converted to voltage by us... View full abstract»

-
48. A CMOS Rectifier With a Cross-Coupled Latched Comparator for Wireless Power Transfer in Biomedical Applications
Publication Year: 2012, Page(s):409 - 413
Cited by: Papers (17)A highly efficient rectifier for wireless power transfer in biomedical implant applications is implemented using 0.18-m CMOS technology. The proposed rectifier with active nMOS and pMOS diodes employs a four-input common-gate-type capacitively cross-coupled latched comparator to control the reverse leakage current in order to maximize the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the rectifier. The des... View full abstract»

-
49. A Delay Locked Loop With a Feedback Edge Combiner of Duty-Cycle Corrector With a 20%–80% Input Duty Cycle for SDRAMs
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):141 - 145A feedback edge combiner is proposed for the duty-cycle corrector (DCC) of a delay locked loop (DLL) to increase the range of allowed input duty cycle. The feedback edge combiner generates the rising edge of a DCC output at the rising edge of an input clock. It generates the falling edge of the DCC output at the rising edge of a feedback clock that is a half-period-delayed signal of the DCC output... View full abstract»

-
50. A Configurable Transmitter Architecture for IEEE 802.11ac and 802.11ad Standards
Publication Year: 2016, Page(s):9 - 13IEEE 802.11ac (WiFi) and IEEE 802.11ad (60-GHz WiGig) are emerging gigabit-per-second standards providing complementary services but different nature of signals. The 802.11ac targets high-resolution and narrow-to-medium bandwidth channels, while 802.11ad aims to provide broadband communications with simple modulation schemes. This work proposes a single-physical-layer transmitter baseband architec... View full abstract»

Aims & Scope
Part I will now contain regular papers focusing on all matters related to fundamental theory, applications, analog and digital signal processing. Part II will report on the latest significant results across all of these topic areas.
Meet Our Editors
Editor-in-Chief
Chi K. Michael Tse
Dept. of Electronic and Information Engineering
Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Hunghom, Hong Kong
cktse@ieee.org


 Abstract
Abstract